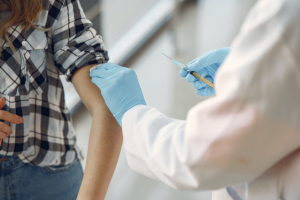
Springtime means time to stop pruning oaks
Fresh pruning wounds of oak trees attract beetles that spread oak wilt. It is critical to not prune oaks from April 15-July 15 in Michigan.

Oak wilt is an aggressive disease that affects many species of oak (Quercus spp.). It is one of the most serious tree diseases in the eastern United States, killing thousands of oaks each year in forests, woodlots and home landscapes. Oaks in the red oak group, distinguished by oak leaves with pointy lobes (Photo 1), are much more susceptible to the disease than white oaks, distinguished by oak leaves with rounded lobes. However, all oaks can be affected.
Oak wilt is a vascular disease that interferes with the tree’s ability to move water from its roots to its leaves. In red oak trees, the disease progresses quickly and trees may be defoliated within weeks of infection (Photo 2).
Oak wilt spreads by two means: overland spread and local spread. In overland spread, sap beetles carry spores from dead trees and infect new trees. Normally a tree’s protective bark is sufficient to protect it from infection, but the beetles are strongly attracted to fresh branch wounds, either from broken branches or pruning cuts, which allow the spores to infect the tree. Because of this, it is critical that homeowners and arborists do not prune oaks from April 15 to July 15 in Michigan. Oak wilt can also spread overland by moving wood. Michigan State University Extension advises to avoid moving wood from trees killed by oak wilt.
In local spread, once a tree is infected with oak wilt, the infection can spread to neighboring trees via root grafts. Therefore it is important to isolate root systems of infected trees, usually by soil trenching or removing stumps.

Photo 2. Oak tree infected with oak wilt. Photo credit: Steve Katovich, US Forest Service Bugwood.org
For more information on oak wilt, see:
- Michigan Oak Wilt Pest Alert, Michigan DNR
- How to Identify, Prevent and Control Oak Wilt, USDA Forest Service
Dr. Cregg’s work is funded in part by MSU’s AgBioResearch.



 Print
Print Email
Email