Food danger zone
Keep food safe by keeping it out of the temperature danger zone.
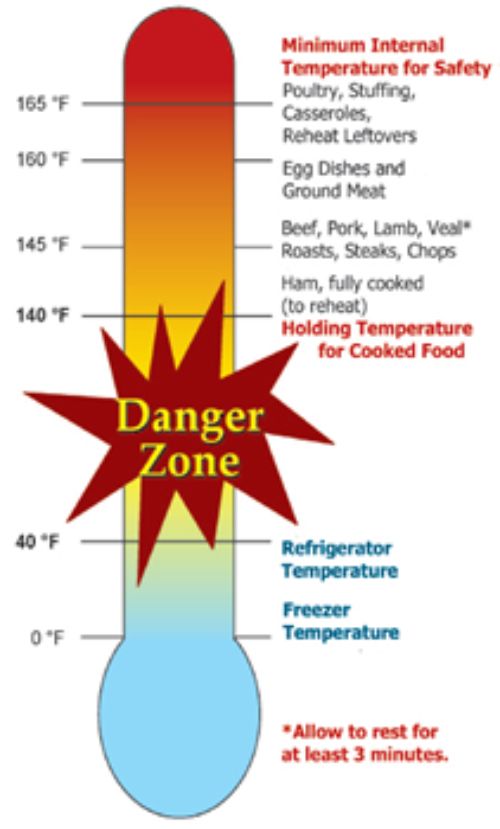
Keeping foods safe means keeping perishable foods out of the temperature danger zone. The temperature danger zone is a temperature range which has been shown to promote and encourage the growth of harmful bacteria in perishable foods. The temperature range for the danger zone is 40-140 degrees Fahrenheit. Our homes, school, offices, etc. are all in the temperature danger zones. When perishable foods are in that temperature range, bacteria growth can occur. Bacterial growth can lead to a foodborne illness. Bacteria double every 20 minutes as foods sit in the danger zone, meaning after a few hours, thousands of bacteria can be present in foods. These huge numbers of bacteria can lead to a foodborne illness for you, a family member or friend.
In order to keep perishable foods safe, they must be stored below or above the danger zone. Michigan State University Extension recommends the following tips:
- Store cold, perishable foods like meat, eggs, leftovers and cut fruit in refrigeration, below 40 degrees Fahrenheit or store them on ice.
- Store hot, perishable foods hot, above 140 degrees Fahrenheit in hot holding equipment (roasters, slow cookers or chafing dishes).
- Use a thermometer in your refrigerator to make sure the temperature is below 40 degrees Fahrenheit. Refrigerators should be held at 38-40 degrees Fahrenheit and must be monitored by a refrigerator thermometer to ensure a safe temperature.
- Use food thermometers when hot holding foods to make sure they stay above the 140 degrees Fahrenheit temperature.
- Foods that have been sitting in the danger zone temperatures for two hours or longer should be discarded. As temperature rise to 90 degrees Fahrenheit or above, foods should only be in the danger zone for one hour before being discarded.
When you are preparing, storing or holding food, keep the temperature danger zone in mind to help you keep your food as safe as possible.
Photo courtesy of U.S. Department of Agriculture.



 Print
Print Email
Email

